IPFS
Gun Control Laws and Enforcement Trends 2023
Written by Sam Jacobs Subject: Gun RightsReport Highlights
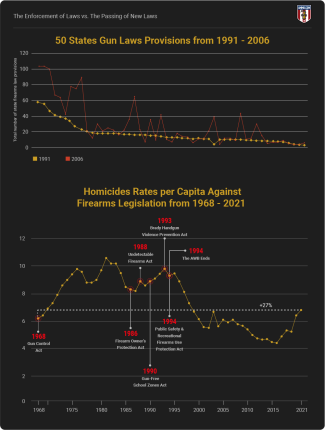
The amount of State gun laws nearly doubled between 1991 and 2016 (Source).
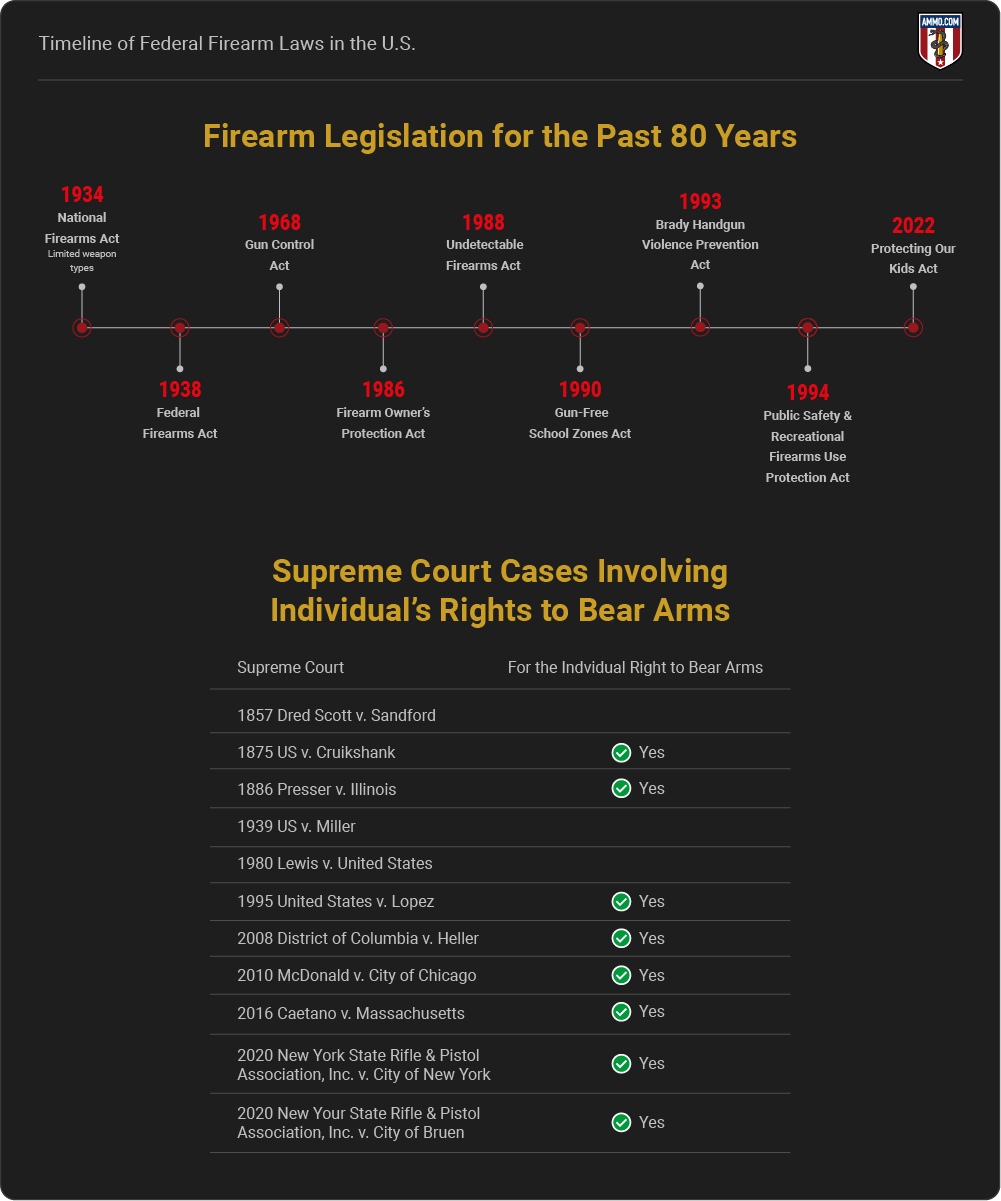
The first Federal gun control law was passed in the 1934 National Firearms Act, which limited civilians' access to machine guns, suppressors, short-barreled shotguns, and others (Source).
Between 1886 and 2023, the Supreme Court of the United States interpreted the Second Amendment to include the right of the individual to keep and bear arms six times.
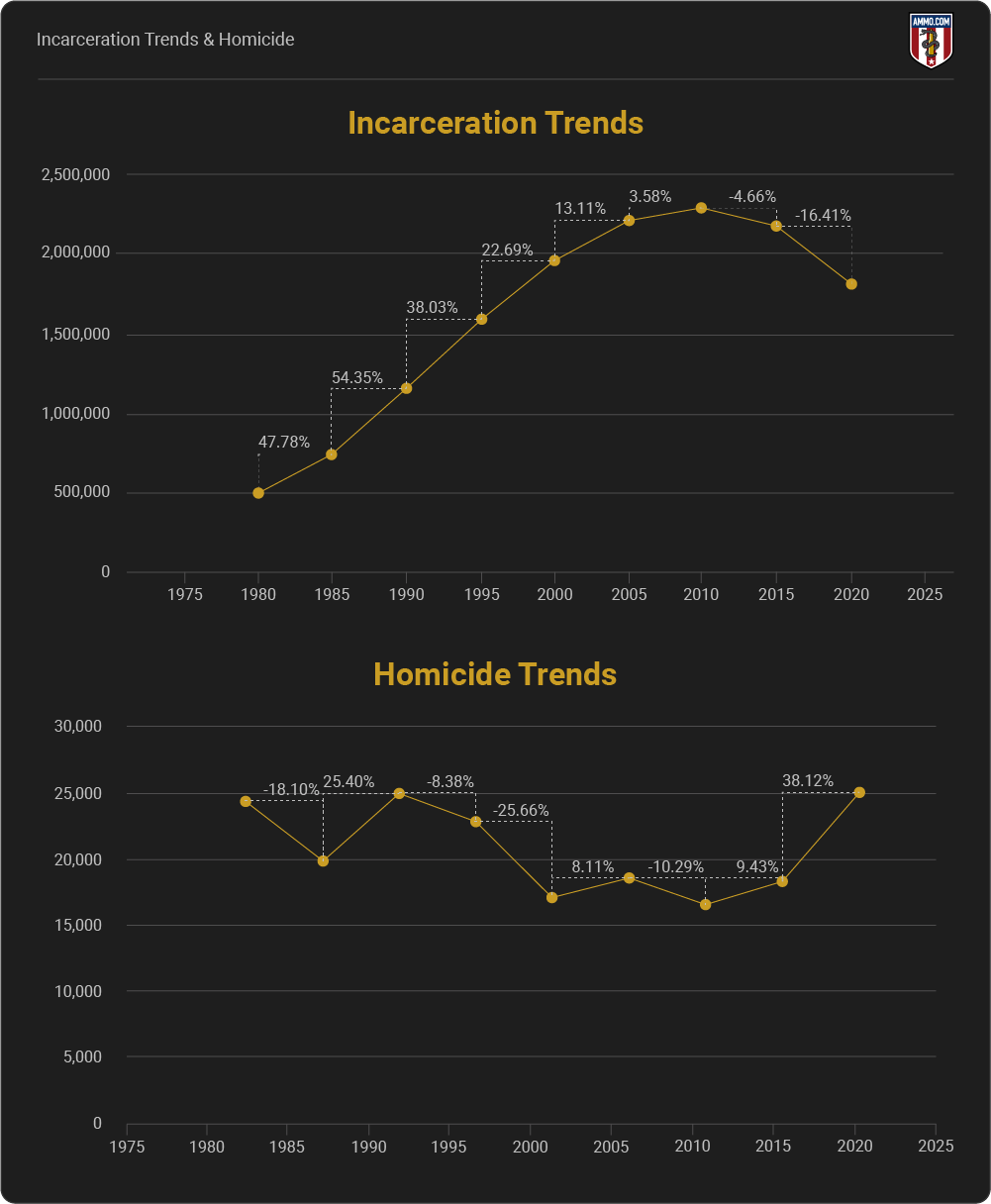
Homicides (all methods) increased 27% from 1968 to 2021.
Homicide rates increased 28% while incarceration rates fell 15% during the 2020 pandemic.
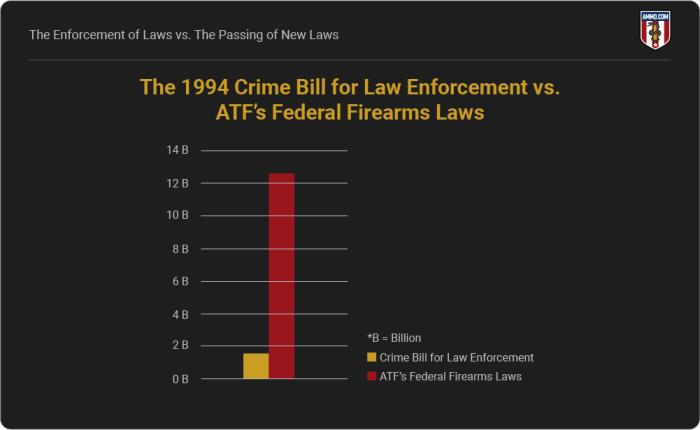
The 1994 Crime Bill authorized $12.5 Billion dollars for law enforcement, while the ATF receives $1.5 billion annually to enforce Federal firearm laws.
The ATF seized more than 360,000 firearms in 2021 (Source).
The Enforcement of Laws vs. The Passing of New Laws
Timeline of Federal Firearm Laws in the U.S.
Laws
1934 National Firearms Act
1938 Federal Firearms Act
1968 Gun Control Act
1986 Firearm Owner's Protection Act
1988 Undetectable Firearms Act
1990 Gun-Free School Zones Act
1993 Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act
1994 Public Safety & Recreational Firearms Use Protection Act
2022 Protecting Our Kids Act
Supreme Court Cases Involving Individual's Rights to Bear Arms
1857 Dred Scott v. Sandford - Determined Slaves do not have 2A rights.
1875 US v. Cruikshank - The right of the individual to keep and bear arms.
1886 Presser v. Illinois - States can ban individuals from forming militias.
1939 US v. Miller - Courts ruled the Federal Government can regulate firearms not effective for militias (i.e. short-barreled shotguns).
1980 Lewis v. United States - Upheld that felons cannot keep and bear arms.
2008 District of Columbia v. Heller - Determined that an individual does not have to be a part of the militia to keep and bear arms.
2010 McDonald v. City of Chicago - Determined that the Due Process Clause of the 14th Amendment also applies to the Second Amendment.
2016 Caetano v. Massachusetts - Determined that the 2nd Amendment applies to firearms that did not exist in 1791.
2020 New York State Rifle & Pistol Association, Inc. v. City of Bruen - Ruled that states must maintain a "Shall-Issue" stance of concealed carry outside of the home.
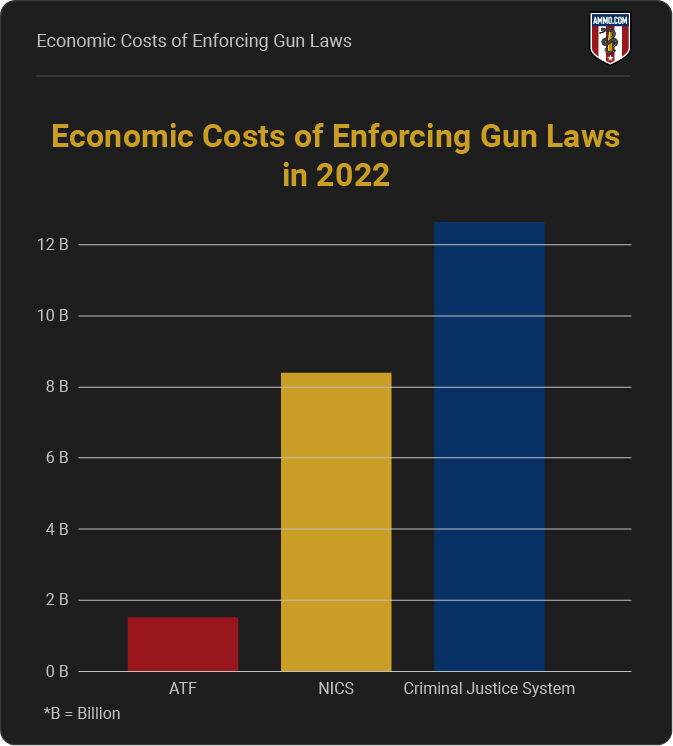
Economic Costs of Enforcing Gun Laws
ATF - 2022 - $1.5 Billion
NICS - 2022 - $8.4 Billion
Criminal Justice System - 2022 - $12.62 Billion
*Compared to $2.8 Billion in medical costs yearly.
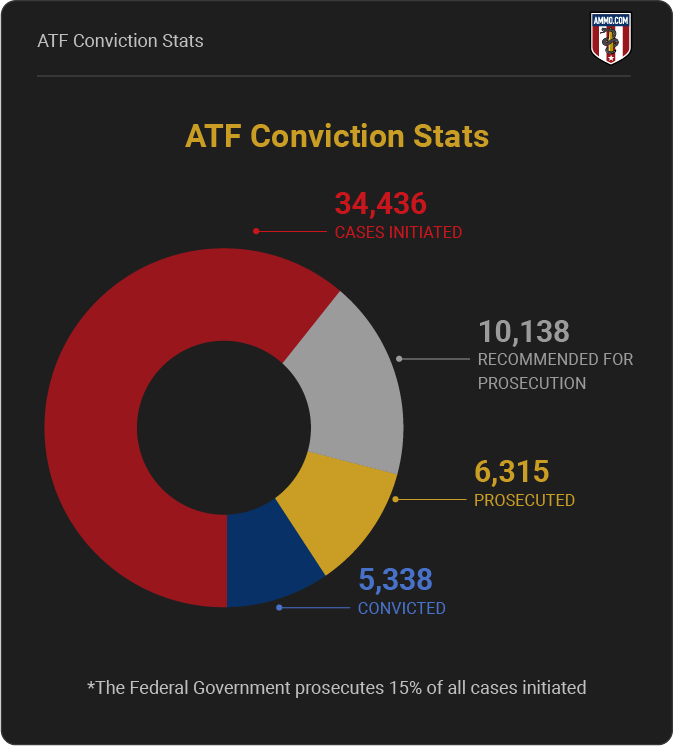
ATF Conviction Stats
34,436 Cases Initiated
10,138 Recommended for prosecution
6,315 Prosecuted
5,338 Convicted
*The Federal Government prosecutes 15% of all cases initiated.
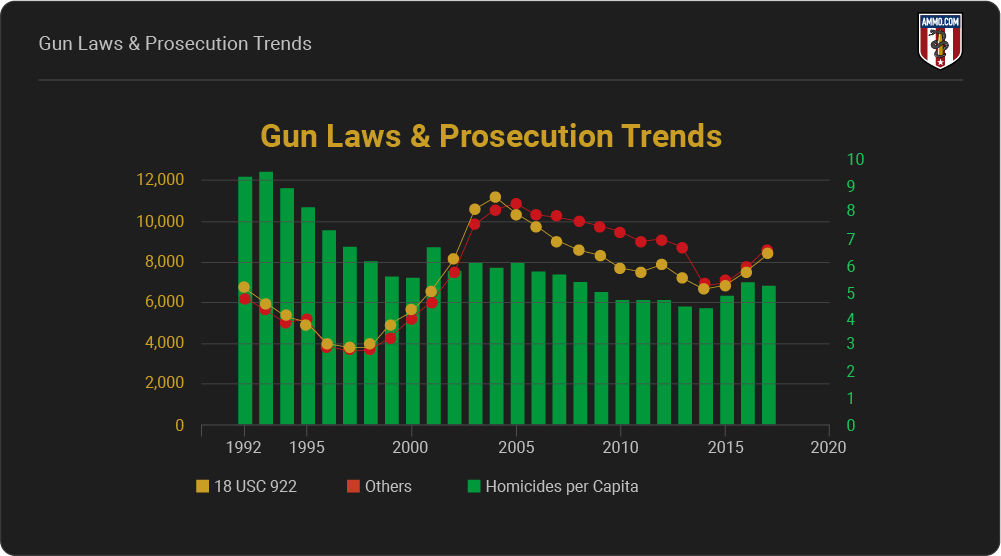
Gun Laws & Prosecution Trends
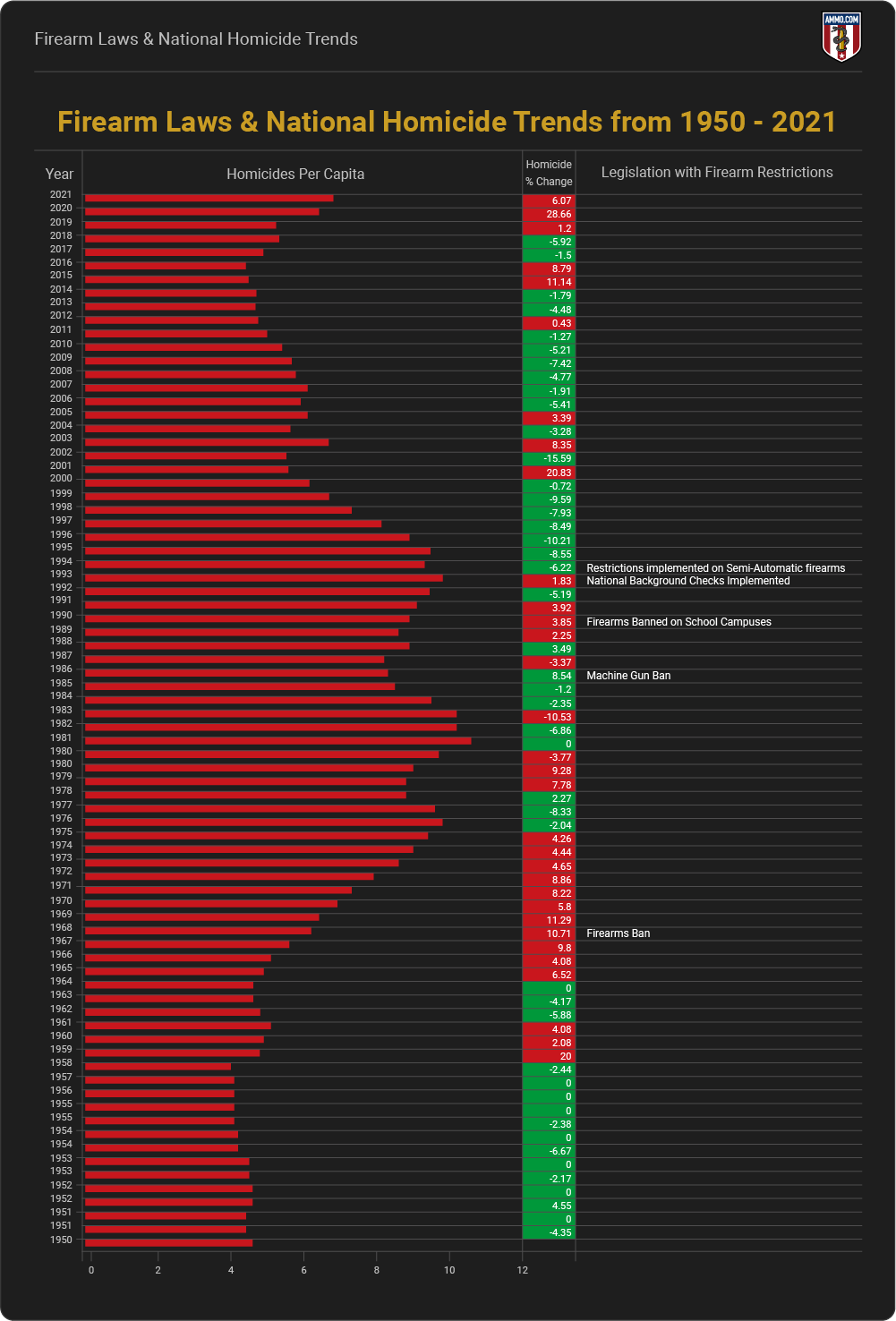
Firearm Laws & National Homicide Trends
Homicides in the U.S. are now 27% higher than before the 1968 Gun Control Act (per capita). They declined by nearly 20% after the 1994 Crime Bill and remained low until 2015. Homicide rates sharply increased in 2019.
Incarceration Trends & Homicide
Sources
Federal Firearm Prosecution Trends
Gun Control Laws and Enforcement Trends 2023 originally appeared in The Resistance Library at Ammo.com.






















