
IPFS News Link • Science, Medicine and Technology
Here's What A Criminology Professor Learned By Studying Every Mass Shooting Since 1966
• https://www.zerohedge.comLast weekend's mass shootings in El Paso and Dayton (following the devastation in Gilroy the weekend before) prompted the usual evidence-free avalanche of political point-scoring, blaming "the other side" for all the world's woes.
"Did George Bush ever condemn President Obama after Sandy Hook. President Obama had 32 mass shootings during his reign. Not many people said Obama is out of Control. Mass shootings were happening before the President even thought about running for Pres." @kilmeade @foxandfriends
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) August 6, 2019
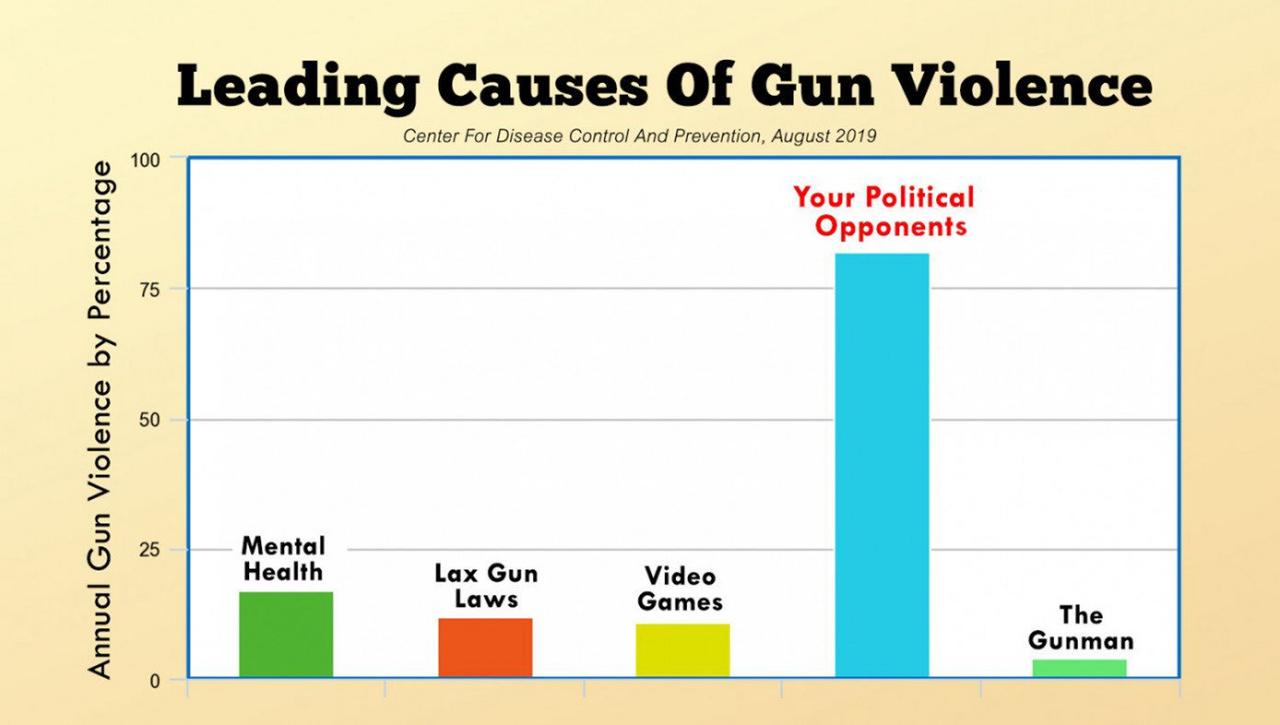
An exhaustive new study from the CDC reveals that the leading cause of gun violence in America is your political opponents. Researchers looked at a number of potential causes of gun violence such as mental health, family situation, cultural shifts, gun laws, rap music, videogames, sugar consumption, and the actual gunman, but by and large, the most prominent cause of gun violence was what most already suspected. The fault lies with those who you disagree with politically.
But, as Jillian Peters and James Densley write in an LA Times op-ed, instead of apportioning blame based on the narrative being pushed, analyzing and understanding data about who commits such massacres can help prevent more lives being lost.
For two years, we've been studying the life histories of mass shooters in the United States for a project funded by the National Institute of Justice, the research arm of the U.S. Department of Justice. We've built a database dating back to 1966 of every mass shooter who shot and killed four or more people in a public place, and every shooting incident at schools, workplaces, and places of worship since 1999. We've interviewed incarcerated perpetrators and their families, shooting survivors and first responders. We've read media and social media, manifestos, suicide notes, trial transcripts and medical records.
Our goal has been to find new, data-driven pathways for preventing such shootings. Although we haven't found that mass shooters are all alike, our data do reveal four commonalities among the perpetrators of nearly all the mass shootings we studied.
First, the vast majority of mass shooters in our study experienced early childhood trauma and exposure to violence at a young age. The nature of their exposure included parental suicide, physical or sexual abuse, neglect, domestic violence, and/or severe bullying. The trauma was often a precursor to mental health concerns, including depression, anxiety, thought disorders or suicidality.
Second, practically every mass shooter we studied had reached an identifiable crisis point in the weeks or months leading up to the shooting. They often had become angry and despondent because of a specific grievance. For workplace shooters, a change in job status was frequently the trigger. For shooters in other contexts, relationship rejection or loss often played a role. Such crises were, in many cases, communicated to others through a marked change in behavior, an expression of suicidal thoughts or plans, or specific threats of violence.
Third, most of the shooters had studied the actions of other shooters and sought validation for their motives. People in crisis have always existed. But in the age of 24-hour rolling news and social media, there are scripts to follow that promise notoriety in death. Societal fear and fascination with mass shootings partly drives the motivation to commit them. Hence, as we have seen in the last week, mass shootings tend to come in clusters. They are socially contagious. Perpetrators study other perpetrators and model their acts after previous shootings. Many are radicalized online in their search for validation from others that their will to murder is justified.
Fourth, the shooters all had the means to carry out their plans. Once someone decides life is no longer worth living and that murdering others would be a proper revenge, only means and opportunity stand in the way of another mass shooting. Is an appropriate shooting site accessible? Can the would-be shooter obtain firearms? In 80% of school shootings, perpetrators got their weapons from family members, according to our data. Workplace shooters tended to use handguns they legally owned. Other public shooters were more likely to acquire them illegally.
So what do these commonalities tell us about how to prevent future shootings?
One step needs to be depriving potential shooters of the means to carry out their plans. Potential shooting sites can be made less accessible with visible security measures such as metal detectors and police officers. And weapons need to be better controlled, through age restrictions, permit-to-purchase licensing, universal background checks, safe storage campaigns and red-flag laws — measures that help control firearm access for vulnerable individuals or people in crisis.
Another step is to try to make it more difficult for potential perpetrators to find validation for their planned actions. Media campaigns like #nonotoriety are helping starve perpetrators of the oxygen of publicity, and technology companies are increasingly being held accountable for facilitating mass violence. But we all can slow the spread of mass shootings by changing how we consume, produce, and distribute violent content on media and social media. Don't like or share violent content. Don't read or share killers' manifestos and other hate screeds posted on the internet. We also need to study our current approaches. For example, do lockdown and active shooter drills help children prepare for the worst or hand potential shooters the script for mass violence by normalizing or rehearsing it?
























1 Comments in Response to Here's What A Criminology Professor Learned By Studying Every Mass Shooting Since 1966
where as I agree with many of his thoughts on the common threads of all the mass shooters, I doubt that red flag laws or licensing requirements will stop the killing. The night club murders in Europe was done with guns and they have very stick gun laws. it didn't stop the murders there. It may however change the tools in which the murders are done. look at England with the trucks used to run people over.